Enterprise GenAI Adoption Solution
Generative AI (GenAI) use cases can be categorized into various groups, including Conversational Interfaces and Business Process automation. Before considering business applications, let’s review the technological challenges of implementing GenAI use cases.
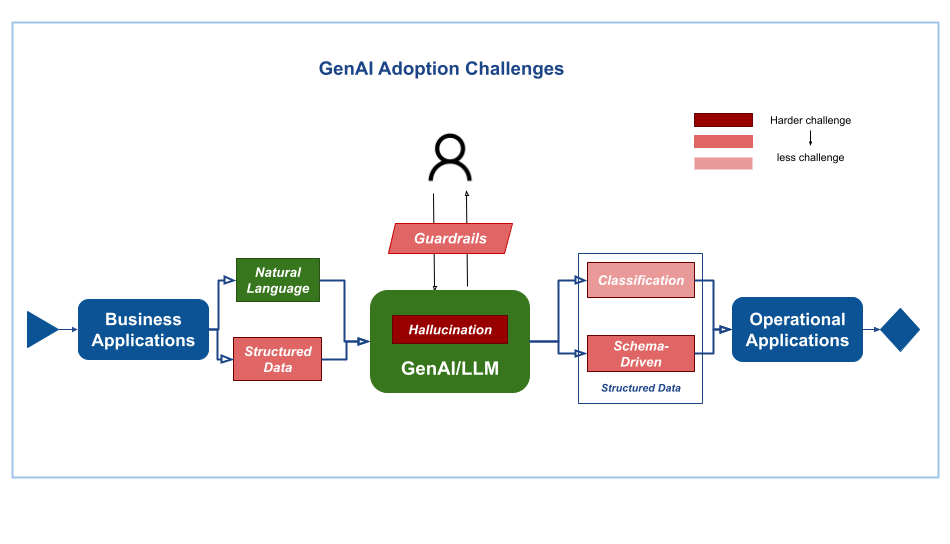
Three main challenges exist:
- Hallucination: GenAI models, like large language models (LLMs), can sometimes provide incorrect or misleading information.
- Governance: There is a lack of mature frameworks to guide responsible interaction between humans and GenAI services.
- Data Integration: When GenAI integrates with existing applications, applications might require data in a specific format that GenAI may not readily generate.
Regardless of the business context, all GenAI adoption efforts will likely face some or all of these challenges.
we will walk you through solutions for each challenges
Hallucination
Hallucination, where LLMs generate inaccurate or misleading text, is a persistent challenge. It can be addressed frfrom three key perspectives:
Large Language Model Training
-
LLM Selection: Choose an LLM trained on a dataset relevant to your task. Consider the model’s foundational training focus (text generation, code creation, etc.) and leverage pre-trained, fine-tuned models whenever possible.
-
Fine-Tuning the Model: If the chosen LLM lacks your specific knowledge, fine-tune it with your own data. This supervised learning process improves the model’s performance on your specific tasks through:
- Data Preprocessing: Ensure your data is clean, formatted appropriately (normalization, feature engineering) to optimize LLM performance.
- Data Security and Privacy: Handle user data securely and adhere to relevant regulations with proper authentication and access controls.
- Instruction Preparation: Clearly define the task, craft concise instructions in natural language, and consider providing relevant examples to guide the model towards the desired outcome.
- Choosing a Fine-Tuning Method: Select the method that aligns with your needs:
- Full Fine-Tuning: Requires a large amount of high-quality data and significant computational resources. Offers the most flexibility and excels in complex tasks, but interpretability of changes is lower.
- PEFT (LoRA): Works well with smaller datasets and is less computationally expensive. May struggle with highly complex tasks and offers less flexibility, but changes are easier to interpret.
- RLHF: Can be effective with limited data but relies heavily on the quality of human feedback. Requires training a separate model and designing good reward functions, which can be challenging. However, RLHF can be effective for complex tasks and offers some interpretability through the separate model.
In-Context Learning
In-context learning allows LLMs to continually learn and adapt based on the specific context of a prompt or query. This can help mitigate hallucination by:
- Prompt Engineering: Craft informative prompts that provide clear context and guide the LLM towards generating factual and relevant outputs. Techniques include:
- Task Specification: Clearly state the desired task within the prompt (e.g., “Write a factual summary of…”)
- Information Provision: Include relevant background information or data points within the prompt to guide the model.
- Example Injection: Provide examples within the prompt to illustrate the desired format or style for the output.
- Few-Shot Learning: Provide a few high-quality examples before the main prompt to prime the LLM for the specific task and reduce the risk of hallucination.
RAG Integration (Retrieval-Augmented Generation)
RAG combines prompt engineering with information retrieval. Here’s how it helps:
- External Knowledge Retrieval: The model retrieves relevant passages from a vast external knowledge base based on the prompt or query.
- Enhanced Context: These retrieved passages provide additional context that the LLM can leverage to generate more accurate and informative outputs.
- Reduced Hallucination: By grounding the generation process in factual information, RAG integration helps reduce the risk of the model resorting to hallucination.
By combining these approaches (selecting the right LLM, fine-tuning, in-context learning, and RAG integration), you can significantly reduce hallucination and ensure your LLM generates reliable and accurate outputs.
Governance
Opening GenAI services to natural language interfaces introduces privacy and safety risks. Implement a governance framework with an orchestration flow and guardrails to manage input and output.
Framework Components
-
Input Orchestration
- Pre-processing
- Data Sanitization: Remove or anonymize sensitive information (e.g., names, addresses) before feeding it to the GenAI model. Techniques like tokenization and differential privacy can be used.
- Intent Recognition: Identify the user’s underlying intent behind their natural language query. This helps route the request to the appropriate GenAI service and reduces the risk of unintended outputs.
- Threat Detection: Scan for malicious queries, hate speech, or attempts to exploit vulnerabilities. Flag or block such queries to protect the system and users.
- Query Routing: Based on the pre-processed input, direct the query to the most suitable GenAI service for handling the specific task. This ensures data relevance and efficient processing.
- Pre-processing
-
Guardrails
- Privacy Policies: Clearly define what data is collected, how it’s used, and user rights regarding their data. Ensure compliance with relevant data privacy regulations (e.g., GDPR, CCPA).
- Output Filtering: Implement filters to prevent the GenAI model from generating outputs that violate privacy (e.g., revealing personal information) or safety (e.g., promoting violence, hate speech). Techniques like keyword blacklisting and bias detection algorithms can be employed.
- Human-in-the-Loop: Integrate human oversight for critical decisions or outputs that carry high risk. Humans can review flagged queries, intervene in sensitive situations, and provide quality control.
-
Output Orchestration
- Post-processing
-
Result Sanitization: Further anonymize or redact sensitive information in the GenAI output before presenting it to the user.
-
Explainability: Provide explanations for the GenAI’s reasoning behind its outputs. This builds user trust and helps identify potential biases. Confidence Scoring: Assign confidence scores to the generated outputs. This helps users assess the reliability of the information and make informed decisions.
-
- Delivery Channels: Tailor the delivery format of the GenAI output based on the user’s needs and the context of the interaction. This could involve text summaries, visualizations, or different language translations.
- Post-processing
-
Continuous Improvement
- Regularly monitor the performance of the governance framework, analyzing user feedback and system logs.
- Update policies, guardrails, and threat detection mechanisms as new risks or privacy concerns emerge.
- Conduct ongoing research to improve data sanitization, explainability techniques, and bias detection algorithms.
Framework Benefits
- Enhanced Privacy: User data is protected through anonymization, access controls, and adherence to privacy regulations.
- Improved Safety: Guardrails prevent the generation of harmful or unsafe outputs, mitigating risks associated with bias and malicious intent.
- Increased Trust: Transparency and explainability build user confidence in the GenAI system.
- Efficient Operations: Input and output orchestration streamline user interactions with GenAI services.
Data Integration
In order to integrate GenAI services with enterprise applications and business process, GenAI models, designed for natural language, need structured data integration. The following is the solution for structured data exchange between GenAI and enterprise applications:
-
Structured Input for GenAI
- Data Preprocessing: Applications should transform their structured data into a format consumable by the GenAI model. This may involve:
- Feature Engineering: Create new features from existing data that better suit the GenAI model’s needs. For instance, convert categorical variables into one-hot encoded vectors.
- Data Cleaning: Ensure data quality by addressing missing values, outliers, and inconsistencies.
- Fine-tuning GenAI Models: When necessary, fine-tune the GenAI model on a dataset of structured data relevant to the enterprise application. This improves the model’s ability to understand and process the specific data format.
- Data Preprocessing: Applications should transform their structured data into a format consumable by the GenAI model. This may involve:
-
Structured Output from GenAI
- Template-based Decoding: During GenAI output generation, employ templates that define the desired structure of the output data. The GenAI model fills in the blanks based on its processing of the input data. This ensures the output adheres to a pre-defined format.
- Conditional Logic: Implement conditional logic within the decoding process to control the structure of the output based on specific conditions within the input data or the generated text itself. This allows for more nuanced and informative structured outputs.
- Post-processing: After generation, further refine the GenAI output to ensure it strictly adheres to the desired data structure. This may involve:
- Data Validation: Validate the output data against predefined schema rules to identify and rectify any formatting errors.
- Data Transformation: Transform the output data into the exact format required by the enterprise application (e.g., conversion between JSON and CSV formats).
-
Continuous Learning
- Feedback Loop: Establish a feedback loop where insights from enterprise application usage can be used to refine GenAI model training data and improve the structured output.
By implementing these solutions, you can bridge the gap between GenAI’s natural language processing capabilities and the structured data requirements of enterprise applications, enabling a seamless flow of information and facilitating GenAI’s participation in business processes.